The next evolution of enterprise automation is here – Agentic AI on AWS. While generative AI focused on creating content and insights, Agentic AI enables intelligent systems to understand, decide, and act within enterprise workflows.
Using Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Q Business, and SageMaker Unified Studio, organizations can build end-to-end agentic systems that operate securely, scale reliably, and remain compliant with enterprise governance.
This article explores the full architecture, use cases, and step-by-step blueprints to help CTOs, AI/ML leaders, and enterprise architects transition from reactive generative AI to proactive, agentic automation.
From Generative to Agentic: The Next Leap in Enterprise AI
Generative AI gave enterprises the ability to create – documents, code, and insights – but every action still needed a human trigger. Agentic AI, as defined in AWS’s prescriptive guidance, takes the next step: enabling systems to reason, plan, and act autonomously while staying within defined guardrails.
The Agentic Process: Understand → Decide → Act
- Understand: The agent interprets data, context, and goals using models like those deployed via Amazon Bedrock.
- Decide: It decomposes a goal into smaller actions, selecting the right tools or APIs.
- Act: It executes these actions across systems, observes results, and reports outcomes.
Agentic AI represents not just a technical upgrade – but an operational revolution where automation becomes adaptive, context-aware, and self-evaluating.
Core AWS Components Behind Agentic AI
1. Amazon Bedrock – The Orchestrator of Intelligent Agents
Amazon Bedrock serves as the foundation of AWS’s agentic capabilities. It offers access to top foundation models and supports Bedrock Agents – intelligent entities that can call APIs, access knowledge bases, and execute actions on behalf of users.
Key Capabilities:
- Tool Invocation: Agents can perform actions through APIs, databases, or external applications.
- Knowledge Bases: They ground responses in enterprise data to reduce hallucination.
- Guardrails: Administrators can configure content filters, PII protection, and output policies.
- Evaluation: Built-in tools help monitor reliability, latency, and safety metrics.
In practice, this means a Bedrock agent can automate tasks like approving invoices, generating compliance reports, or updating CRM data – all under secure, auditable AWS infrastructure.
2. Amazon Q Business – The Intelligent Enterprise Assistant
Amazon Q Business extends these capabilities into ready-to-deploy enterprise assistants. It combines retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with agentic workflows that help organizations query, analyze, and act on business data securely.
Highlights:
- RAG + Workflow Automation: Q Business retrieves data from multiple enterprise systems, reasons about it, and executes structured responses.
- Task Decomposition: It can break down complex questions (like “Summarize quarterly sales by region”) into smaller retrieval and reasoning steps.
- Governance: Role-based access, audit trails, and permissions ensure enterprise security.
- Explainability: Each response is traceable, showing which documents or systems were referenced.
For enterprises, Q Business can automate knowledge discovery, reduce manual analysis, and provide employees with a conversational interface for enterprise data.
3. SageMaker Unified Studio – The Engine for Development and Governance
SageMaker Unified Studio brings these components together in a single, governed environment. It supports full lifecycle management – from model building and evaluation to deployment and monitoring of agentic systems.
Capabilities:
- Unified workspace for developers, data scientists, and ML engineers.
- Integration with Bedrock and Q Business for building and managing agents.
- Built-in CI/CD pipelines, governance controls, and collaborative tools.
- Real-time evaluation dashboards for safety, cost, and performance metrics.
For organizations seeking both agility and control, SageMaker Unified Studio provides the environment to experiment with generative models, test agentic behaviors, and deploy them responsibly.
Building an Agentic AI Architecture on AWS
Event-Driven Orchestration
Agentic workflows typically run through event triggers. For instance:
- A new ticket in ServiceNow triggers a Bedrock agent that retrieves context, drafts a response, and updates the CRM.
- A financial anomaly in a data lake triggers an agent that evaluates, recommends mitigation, and alerts compliance.
AWS EventBridge or Step Functions can be used for orchestration, ensuring reliable sequencing and error recovery.

Tool Connectivity and Permission Boundaries
Each agent operates within its own IAM role – defining what it can access or modify. Bedrock’s Guardrails ensure content and actions remain compliant, while audit trails track every agent decision for accountability.
Observability and Human-in-Loop
To maintain trust, enterprises must observe agent behavior:
- Use CloudWatch and CloudTrail for monitoring.
- Define reliability gates and escalation rules when an agent’s confidence drops below a threshold.
- Integrate human-in-loop validation for high-impact decisions like approvals or compliance actions.
Implementation Blueprint: Step-by-Step
- Set up environment:
Establish AWS accounts, IAM roles, and monitoring using CloudWatch and CloudTrail. - Prepare data:
Ingest and clean enterprise data, define knowledge bases, and ensure PII masking. - Select foundation model:
Choose from Bedrock’s curated models (like Anthropic Claude or Mistral) based on task complexity. - Configure agent roles:
Define purpose, tool access, and guardrails for each agent in Bedrock or Q Business. - Design workflow:
Map triggers, actions, and APIs using Bedrock Flows or Step Functions. - Enable governance:
Apply Guardrails for moderation, role-based access, and observability. - Evaluate performance:
Track task success, latency, intervention rate, and cost per action. - Deploy in SageMaker Unified Studio:
Use CI/CD pipelines for testing and promotion to production. - Run pilot program:
Test within a specific team or region (for example, APAC) with rollback options. - Scale and monitor:
Expand to more workflows, monitor KPIs, and iterate safely.
Download the Implementation Checklist (PDF) – for quick setup and validation.
Real-World Use Cases
Finance – Automated Risk Analysis
Input: Transaction data and portfolio rules.
Agent Workflow: Detect anomalies, retrieve historical data, recommend risk mitigation, and trigger compliance review.
Outcome: 40% reduction in manual risk triage time.
Retail – Intelligent Inventory Management
Input: Real-time sales and stock levels.
Agent Workflow: Forecast demand, generate purchase requests, and update ERP system.
Outcome: 15% reduction in stockouts and 8% increase in margin.
Healthcare – Clinical Data Summarization
Input: Patient reports and medical guidelines.
Agent Workflow: Retrieve relevant data, generate treatment summary, and prepare discharge note.
Outcome: 20% faster report generation with human validation.
Risks and Cost Considerations
Potential Risks:
- Model hallucination – controlled using RAG grounding and guardrails.
- Data exfiltration – prevented through strict IAM boundaries.
- Prompt injection – mitigated by input validation and content filters.
- Cost overrun – managed through tracking, throttling, and budget alerts.
- Over-automation – offset by keeping humans in oversight loops.
Cost Control Tips:
- Use smaller models for routine tasks.
- Monitor per-action costs using CloudWatch metrics.
- Use SageMaker cost analysis for agent workloads.
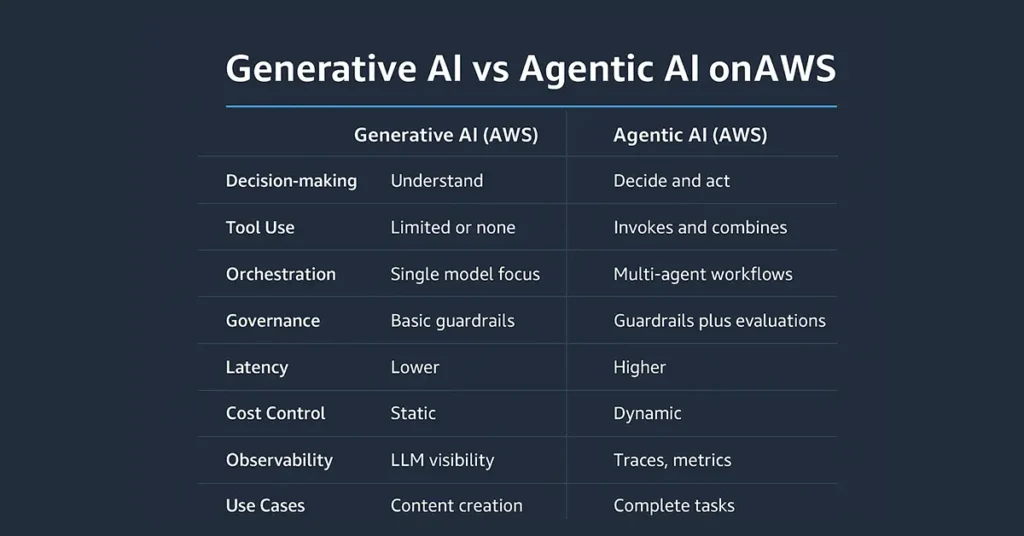
Generative vs Agentic AI on AWS
| Dimension | Generative AI (AWS) | Agentic AI (AWS) | Notes for Architects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | Reactive responses | Goal-oriented planning and action | Requires orchestration logic |
| Tool Use | Limited or manual | Automated via APIs and systems | Set permissions per agent |
| Governance | Output filtering | Full lifecycle governance | Use IAM + Guardrails |
| Observability | Prompt logs only | Full decision and trace logs | Enable CloudTrail |
| Cost Control | Model-based billing | Action + orchestration costs | Apply cost ceilings |
| Use Cases | Content creation, Q&A | End-to-end automation | Choose based on need |
Implementation Checklist
- Define business objective and KPIs.
- Set up AWS account and IAM permissions.
- Prepare and ground enterprise data.
- Choose foundation models from Bedrock.
- Configure agent logic and guardrails.
- Design and test workflows in Bedrock Flows.
- Implement observability and human-in-loop checkpoints.
- Evaluate task success and reliability metrics.
- Run pilot deployment with rollback plan.
- Scale to production and monitor cost ceilings.
Key KPIs to Track
- Task success rate – percentage of successful automated tasks.
- Intervention rate – how often human review is required.
- Latency SLO – average completion time per task.
- Cost per action – unit economics of each workflow.
- Safety compliance – violations per 1,000 agent actions.
- System uptime – percentage of workflows executed without failure.
FAQs
1. What makes Agentic AI different from Generative AI?
Agentic AI can plan and take actions autonomously, while generative AI only responds with outputs.
2. Why use AWS for Agentic AI?
AWS offers an end-to-end stack – Bedrock for models, Q Business for workflows, and SageMaker Unified Studio for governance and deployment.
3. How does Agentic AI ensure security?
Through IAM roles, Guardrails, audit trails, and content moderation policies.
4. Is Agentic AI suitable for enterprises in India/APAC?
Yes, AWS provides regional availability, data sovereignty, and localized compliance frameworks.
5. What’s the best way to start?
Run a pilot using Bedrock agents and evaluate with KPIs like latency, success rate, and intervention frequency.
6. Can I integrate existing systems?
Yes, AWS agents can connect to CRMs, ERPs, APIs, and data lakes using Bedrock tools or Q Business connectors.
Conclusion
Agentic AI AWS represents the future of enterprise automation – where systems don’t just answer but act. By combining Amazon Bedrock’s orchestration, Q Business’s enterprise retrieval, and SageMaker Unified Studio’s lifecycle management, organizations can deliver automation that’s intelligent, traceable, and governed.
Start with a pilot, define your guardrails, track your KPIs, and scale responsibly. The businesses that adopt agentic systems today will lead tomorrow’s automation revolution.
